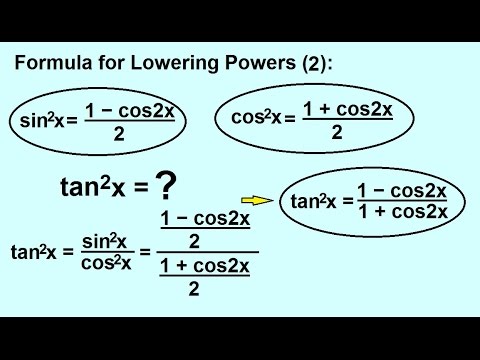
Account Details Login Options Account Management Settings · The power reducing identities allow you to write a trigonometric function that is squared in terms of smaller powers The proofs are left as examples and review problems \(\sin ^2x=\dfrac{1−\cos 2x}{2}\) \(\cos ^2x=\dfrac{1\cos 2x}{2}\) \(\tan ^2x=\dfrac{1−\cos 2x}{1\cos 2x}\) Power reducing identities are most useful when you are asked to rewrite expressions suchTan^2x = sin^2x/cos^2x 13K views Sponsored by Neat A/B Testing 5 minutes can result in exponential learnings for your store
Bestmaths Online Proof 4
Tan 2x identity
Tan 2x identity-The Trigonometric Double Angle identities or Trig Double identities actually deals with the double angle of the trigonometric functions For instance, Sin2(α) Cos2(α) Tan2(α) Cosine2(α) Sec2(α) Cot2(α) Double Angle identities are a special case of trig identities where the double angle is obtained by adding 2 different angles In this article, we will cover upTrig Identities Identities involving trig functions are listed below Pythagorean Identities sin 2 θ cos 2 θ = 1 tan 2 θ 1 = sec 2 θ cot 2 θ 1 = csc 2 θ Reciprocal Identities Ratio Identities Odd/Even Identities sin (–x) = –sin x cos (–x) = cos x tan (–x) = –tan x csc (–x) = –csc x sec (–x) = sec x cot (–x) = –cot x Cofunction Identities, radians
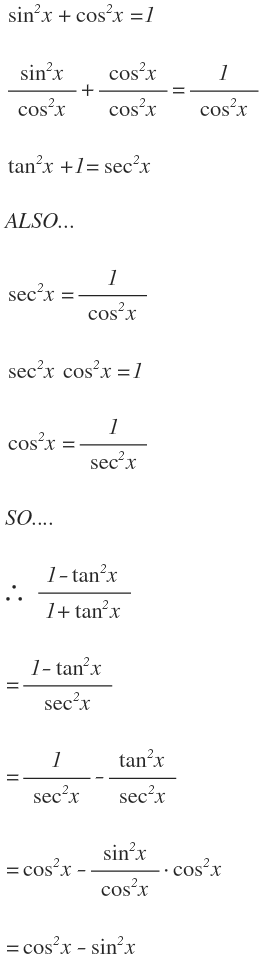


How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic
Free math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly · The identity `tan^2 x = (1 cos(2x))/(1 cos(2x))` has to be proved Use the relation `cos(2x) = 2*cos^2x 1 = 1 2*sin^2x` `(1 cos(2x))/(1 cos(2x))`$$2\cot4x = \cot2x \tan2x$$ Thank you in advance Thank you for the comments and hints I got an answer after many tries ;) Below is my answer Thank you $2cot4x = cot2x tan2x$ $2\frac{1}{tan 4x} = cot2x tan2x$ $2\frac{1}{\frac{2 tan 2x}{1 tan^2 2x}} = cot2x tan2x$
One to one online tuition can be a great way to brush up on your Maths knowledge Have a Free Meeting with one of our hand picked tutors from the UK's top universitiesI'm not sure if I should be working on the right side of the equation instead!Proofs of Trigonometric Identities I, sin 2x = 2sin x cos x That's all it takes It's a simple proof, really What is the formula for cos 2a?
Tan^4 (x) 1 or (tan^2(x)1)(tan^2x1) then i'm stuck! · How to prove the trigonometry equation is an identity?Proving Trigonometric Identities Calculator online with solution and steps Detailed step by step solutions to your Proving Trigonometric Identities problems online with our math solver and calculator Solved exercises of Proving Trigonometric Identities Calculators Topics Solving Methods Go Premium ENG • ESP Topics Login Tap to take a pic of the problem calculators


Tan 2x Sec 2x Youtube


Trigonometric Identity With Pythagorens Sec 2x Sin 2x Cos 2x Tan 2x Youtube
· Yes, sec2 − 1 = tan2x is an identityTanx = t Sec^2 xdx= dt So now it is, 1/ (1t)^2dt This integral is given by 1/1t and t= tanx So, it is cosx/cosx sinx Integral of the function 1tanxcos2x https//mathstackexchangecom/q/ Let I = ∫ 1tanxcos2xIn this video, we are going to derive the identity for the tangent of 2xThe identity for tan(x y) has been explained in the following videohttps//youtub
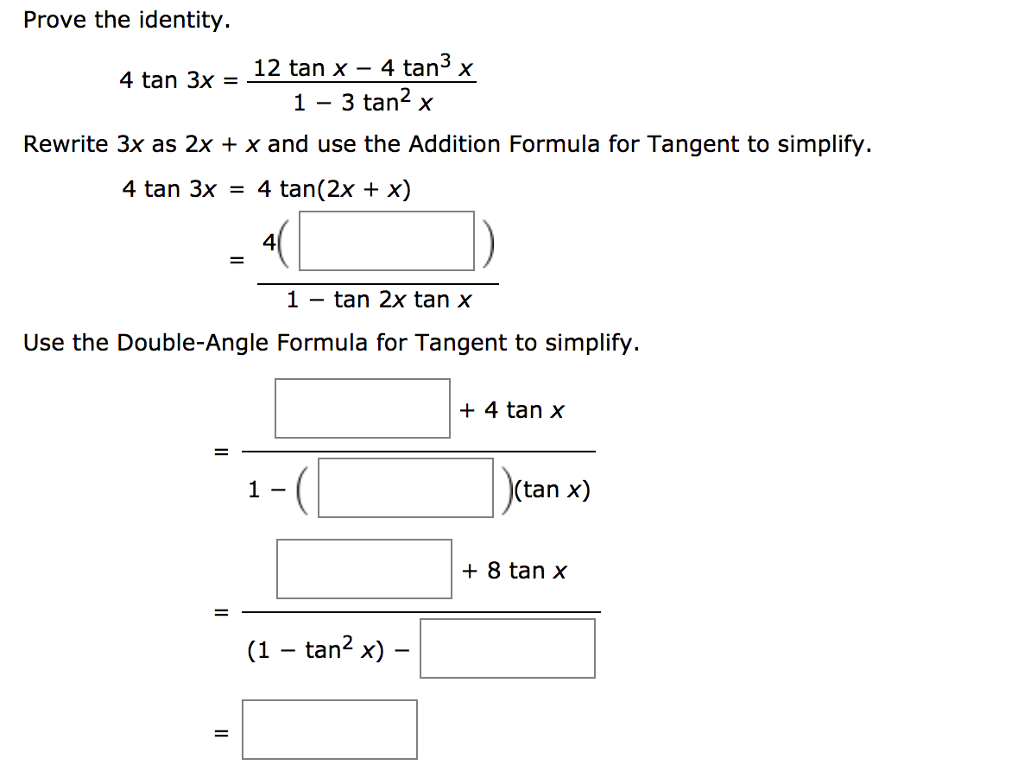


Solved Prove The Identity 4 Tan 3x 12 Tan X 4 Tan 3 Chegg Com



Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo
Identities expressing trig functions in terms of their supplements Sum, difference, and double angle formulas for tangent The half angle formulas The ones for sine and cosine take the positive or negative square root depending on the quadrant of the angle θ/2 For example, if θ/2 is an acute angle, then the positive root would be used Truly obscure identities These are just here forTranscribed image text Verify the identity tan?zx sin ?2x cos2x = secax To verify the identity, start with the more complicated side and transform it to look like the other side Choose the correct transformations and transform the expression at each step tan 2x sin 2x cos2x sec?Simply note that the following identity holds \tan 2x =\frac{2\tan x}{1\tan^2 x} which can be easily checked by the following \tan{2x}=\frac{\sin {2x}}{\cos{2x}} \sin{2x}=2\sin x\cos x \cos{2x}=\cos^2{x}\sin^2{x}
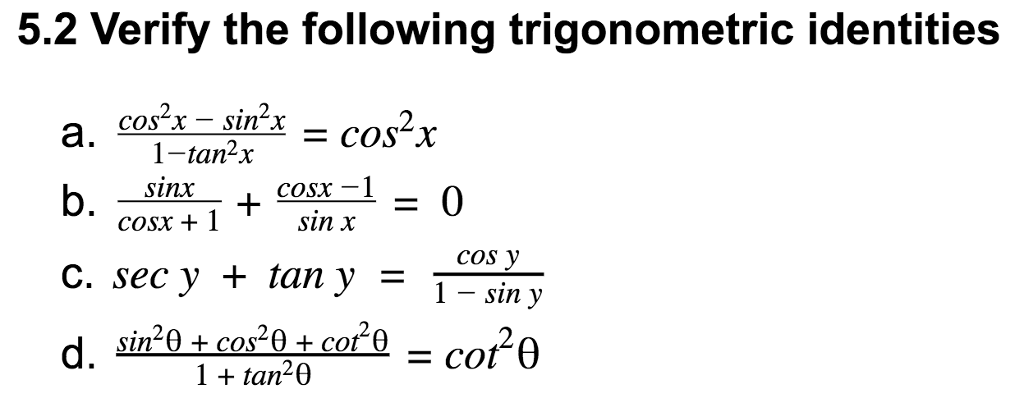


Solved 5 2 Verify The Following Trigonometric Identities Chegg Com
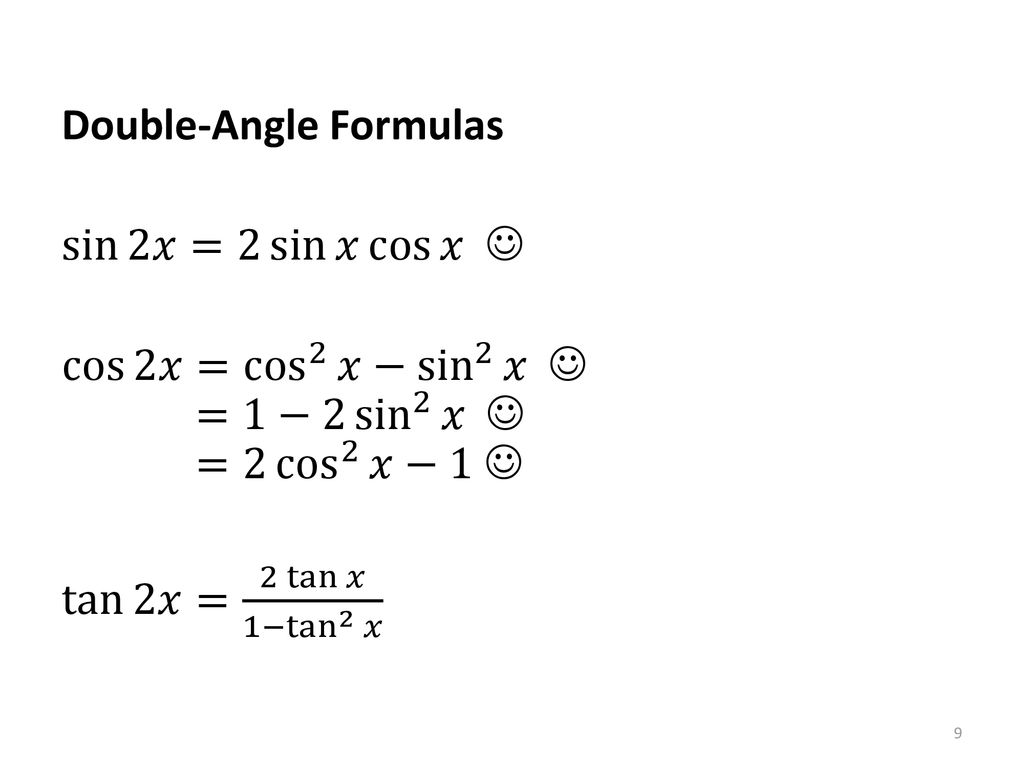


Packet 21 Trigonometric Identities Ppt Download
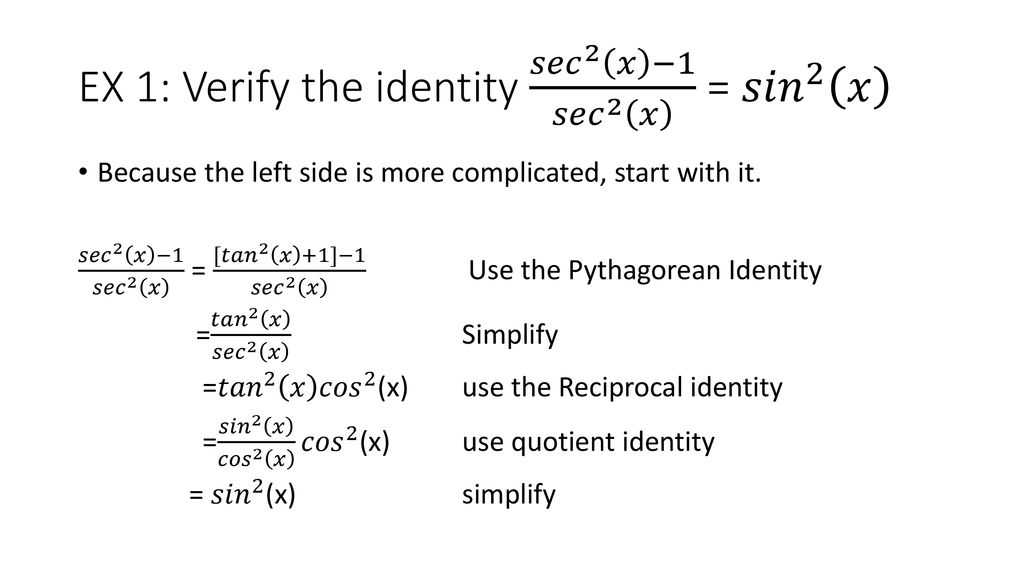
Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution Physics Mechanics ChemistryChoose the correct transformations and transform the expression at each step tan?zx sin 2x cos2x Factor out the greatest common factor Apply a Pythagorean identity to the sum of the second and third term Apply a Pythagorean identity to the sum of the first and second term Express in terms of sines and cosines Verify the identity tan 2x sin 2x cos2x = secx To verifyThe Pythagorean identity tells us that no matter what the value of θ is, sin²θcos²θ is equal to 1 We can prove this identity using the Pythagorean theorem in the unit circle with x²y²=1 The Pythagorean identity tells us that no matter what the value of θ is, sin²θcos²θ is equal to 1 We can prove this identity using the Pythagorean theorem in the unit circle with x²y²=1 If
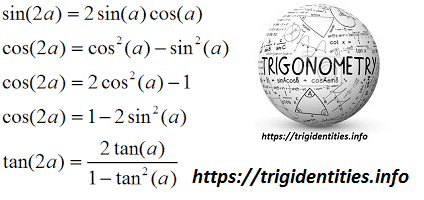


Trig Double Identities Trigonometric Double Angle Functions Trig



Cos2x Sin2x 1 1 Tan2x Sec2x Cot2x 1 Csc2x Cofunction
X tan 2 x = sec 2 x I started this by making sec 1/cos and using the double angle identity for that and it didn't work at all in any way everNeed help with Maths?We try to relate the given equation to one of our three identities We can use the identity sec2 x = 1tan2 x to rewrite the equation solely in terms of tanx 2tan2 x = sec2 x 2tan 2x = 1tan x from which tan2 x = 1 Taking the square root then gives tanx = 1 or − 1 The graph of tanx between 0 and 2π is shown in Figure 2 Note that the
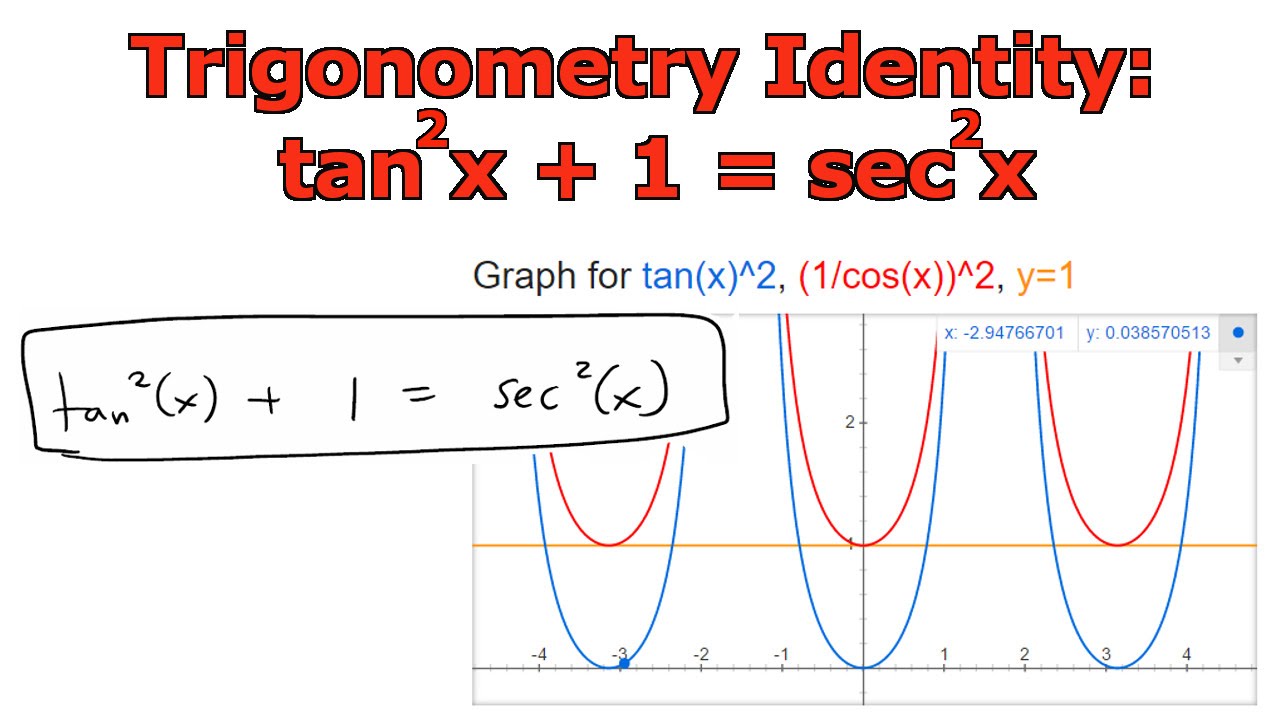


Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube


Double Angle And Half Angle Identities Example Sin 28 Cos 2a Or Tan 2x
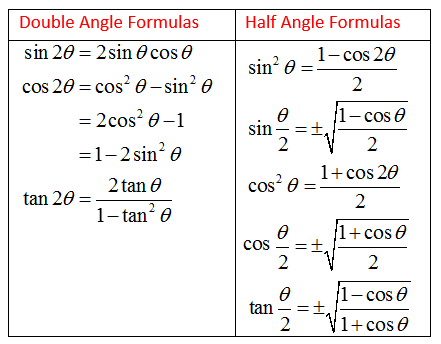
1)View Solution 2)View SolutionPart (i) Part (ii) 3)View Solution 4)ViewThe half‐angle identity for tangent can be written in three different forms In the first form, the sign is determined by the quadrant in which the angle α/2 is located Example 5 Verify the identity Example 6 Verify the identity tan (α/2) = (1 − cos α)/sin α Example 7 Verify the identity tan (α − 2) = sin π/(1 cos α) Begin with the identity in Example 6 Example 8 Use a · Double angle identities and formulae are useful for solving certain integration problems where a double formula may make things much simpler to solve Therefore in mathematics as well as in physics, such formulae are useful for deriving many important identities The trigonometric formulas like Sin2x, Cos 2x, Tan 2x are popular as double angle formulae,



Tan 2x Identity Learn Lif Co Id


Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x
Tan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos 2 (x) sin 2 (x) = 2 cos 2 (x) 1 = 1 2 sin 2 (x) tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1Identities related to sin 2x, cos2x, tan 2x, sin3x, cos3x, and tan3x 1 Sin 2x = Sin 2x = sin (2x)=2sin (x) cos (x) Sin (2x) = 2 * sin (x)cos (x)Factor out the greatest common factor Apply a Pythagorean Identity to the sum of the second and third


Biomath Trigonometric Functions


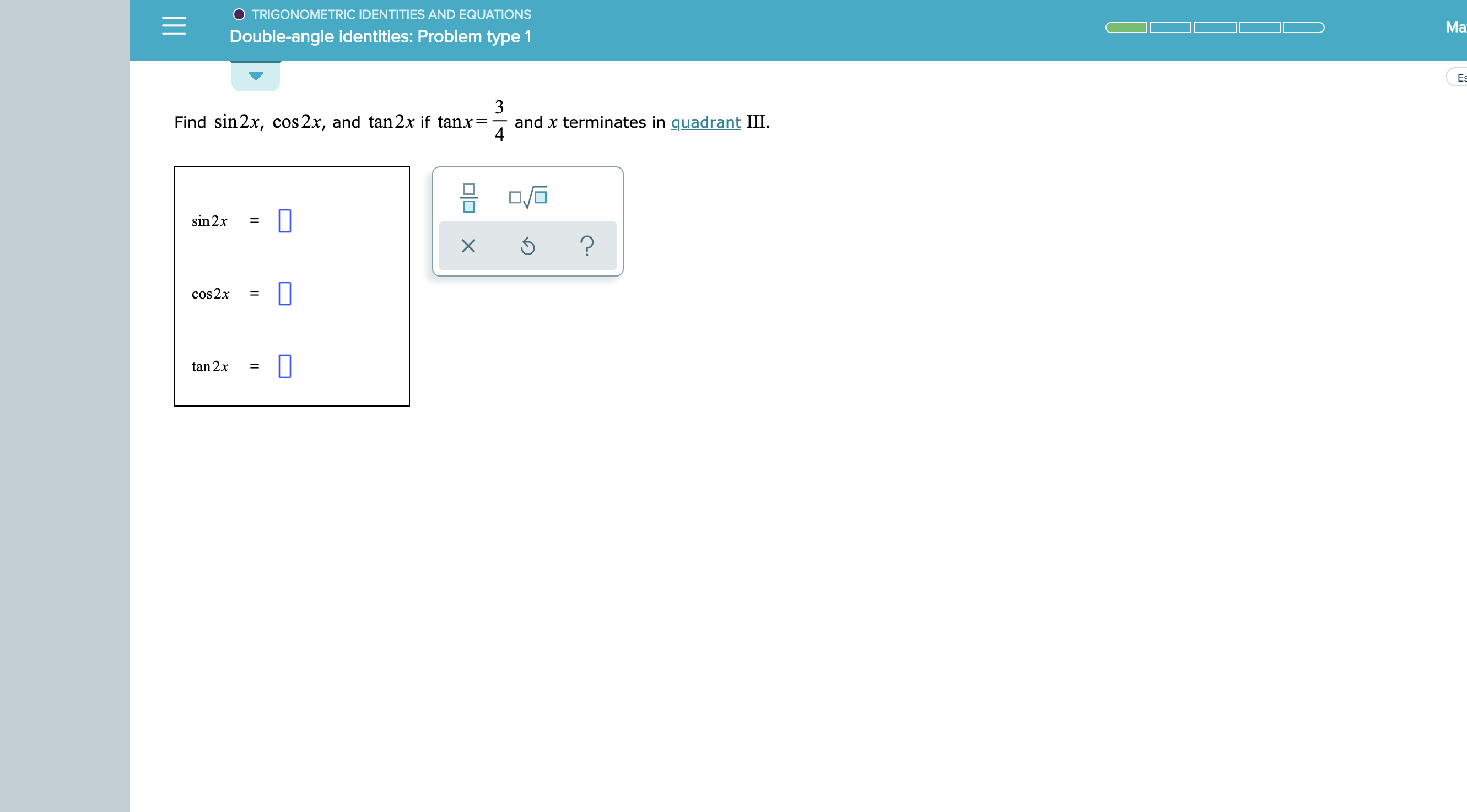
How To Find Sin2x Cos2x And Tan2x If Tanx 3 4 And X Terminates Quadrant I Quora
From the graph we see that x = 0 is a solution corresponding to that part of the equation cosx =1 Awellknownresultisthatcos π 3 = 1 2Sin 2x, Cos 2x, Tan 2x is the trigonometric formulas which are called as double angle formulas because they have double angles in their trigonometric functions Let's understand it by practicing it through solved example \(Tan 2x =\frac{2tan x}{1tan^{2}x} \)In this video you will learn how to verify trigonometric identitiesverifying trigonometric identitieshow to verify trig identitieshow to verify trigonometric


Integrate Sec 2x Method 1



What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora
Various identities and properties essential in trigonometry Legend x and y are independent variables, d is the differential operator, int is the integration operator, C is the constant of integration Identities tan x = sin x/cos x equation 1 cot x = cos x/sin x equation 2 sec x = 1/cos x equation 3 csc x = 1/sin x equation 4 cot x = 1/tan x equation 5 sin 2 x cos 2 x = 1Notebook Groups Cheat Sheets;Answer to Use a doubleangle identity to find tan(2x) \ if \ sec \ x = \sqrt {14} \ and \ sin \ x < 0 tan(2x)= By signing up, you'll get


Solved Prove The Identity Cot 2x 1 Tan2 X 2 Tan X Chegg Com


A Trig Identity
Free multiple angle identities list multiple angle identities by request stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy Learn more Accept Solutions Graphing Practice;B) (tanx 1)(tanx1)/1 tan^2(x) = (sinx/cosx 1)(sinx/cosx 1) / 1/cosx then again I'm stuck!The formula cos 2A = cos2 A − sin which is yet a third form


How Does One Verify Cos 2x Sin 2x 1 Tan 2x Cos 2x Socratic
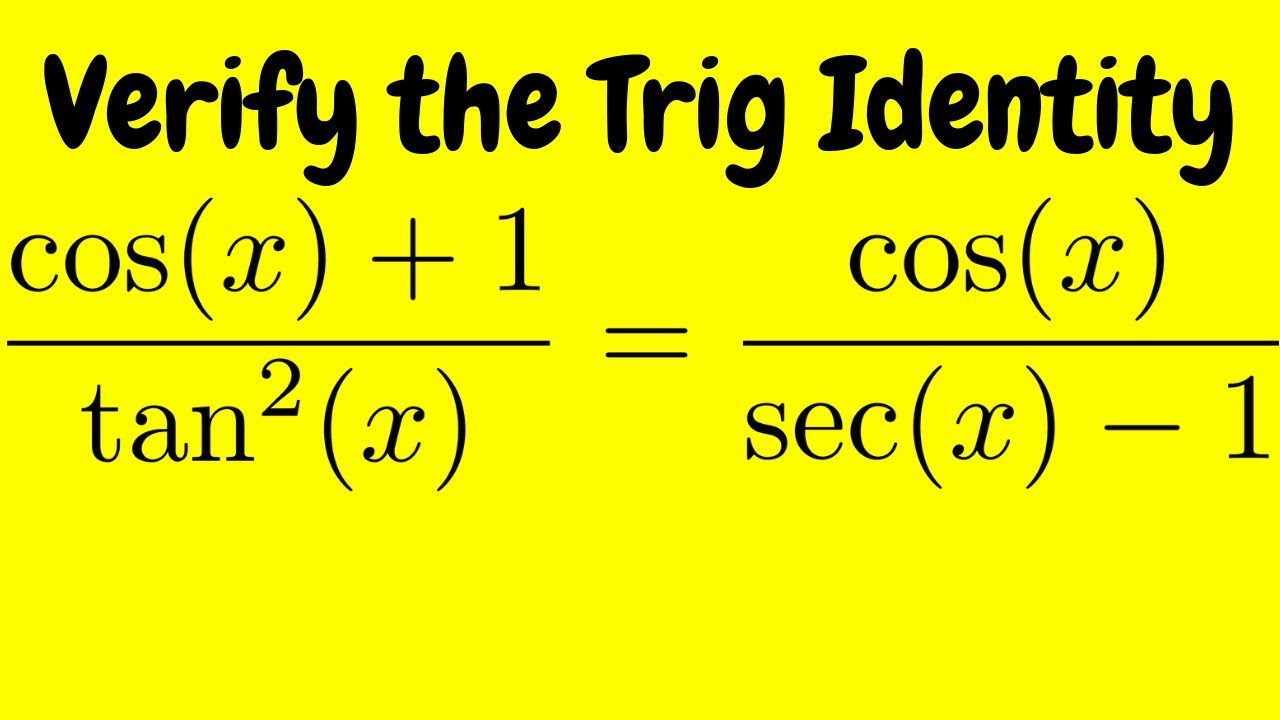


Verifying A Trigonometric Identity Cos X 1 Tan 2 X Cos X Sec X 1 Youtube
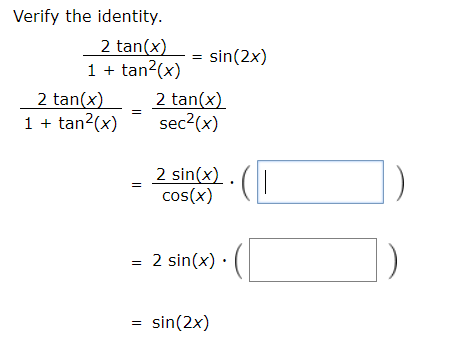
The Pythagorean identity of secant and tan functions can also be written popularly in two other forms $\sec^2{x}\tan^2{x} \,=\, 1$ $\sec^2{A}\tan^2{A} \,=\, 1$ Remember, the angle of a right triangle can be represented by any symbol but the relationship between secant and tan functions must be written in that symbol Proof Learn how to prove the Pythagorean identity of secantUsing the Pythagorean identity, sin 2 αcos 2 α=1, two additional cosine identities can be derived and The half‐angle identities for the sine and cosine are derived from two of the cosine identities described earlier The sign of the two preceding functions depends on the quadrant in which the resulting angle is located Example 1 Find the exact value for sin 105° using the halfAnswer to Establish the identity {2 tan x} / {2 sec^2 x} = tan 2x By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your



Art Of Problem Solving



Solved Verify The Identity 4 2 Tan X Secx2tan X 1 Whic Chegg Com
· Keeping this in consideration, what is the identity of sin 2x? · These identities are sometimes known as powerreducing identities and they may be derived from the doubleangle identity \(\cos(2x)=\cos^2x−\sin^2x\) and the Pythagorean identity \(\cos^2x\sin^2x=1\)Prove the identity ` ``(tan^2x)/(1tan^2x)=sin^2x ` Note that `tan^2x1=sec^2x=1/(cos^2x) ` and `tan^2x=(sin^2x)/(cos^2x) ` Substituting we get
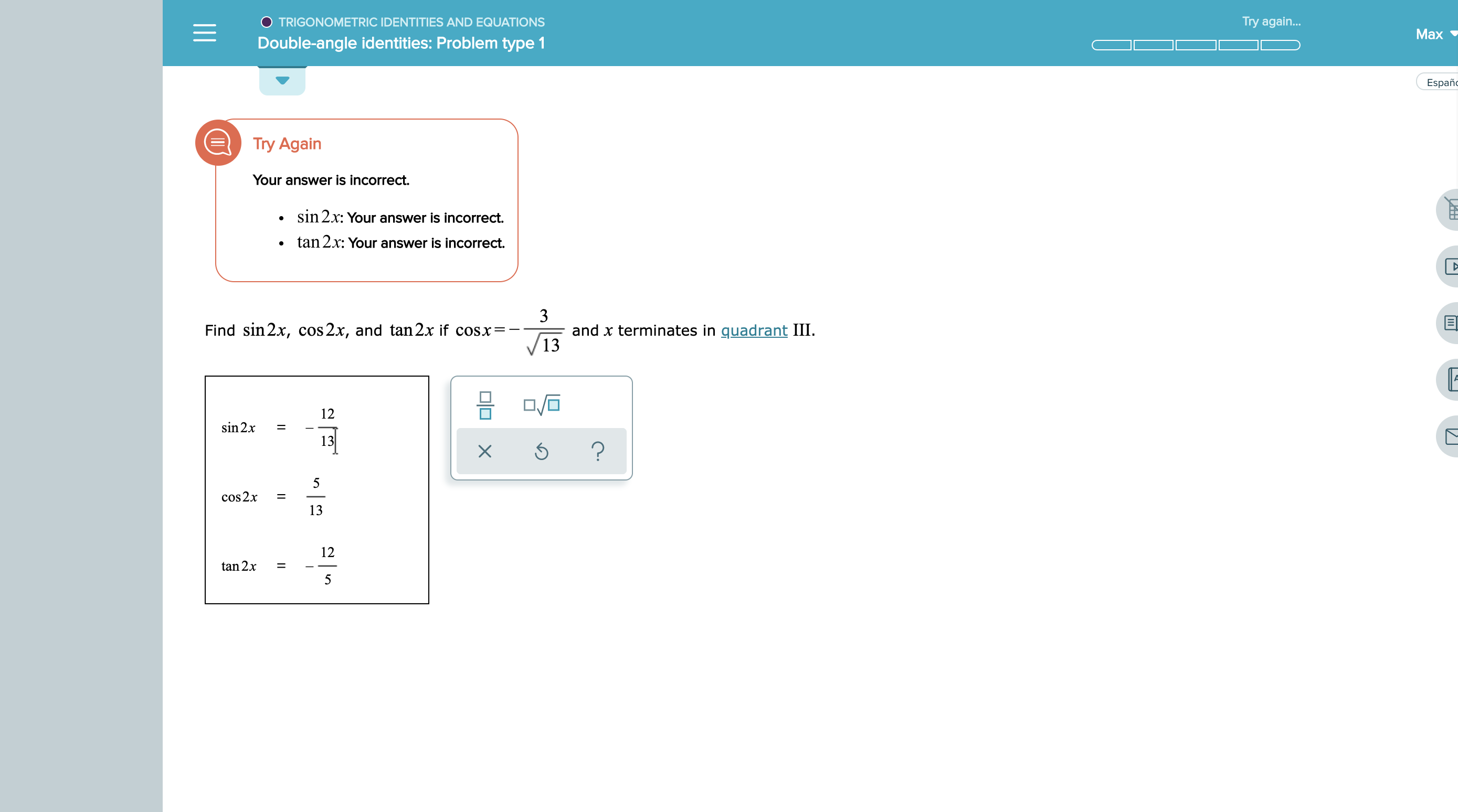


Answered Try Again Trigonometric Identities Bartleby
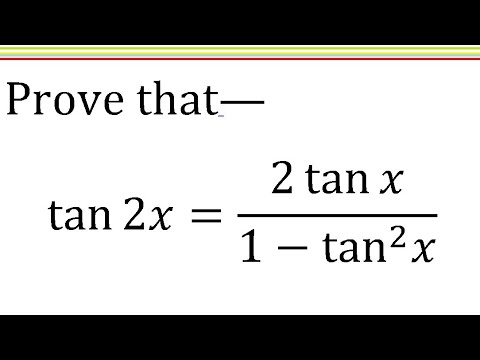


Tan2x 2tanx 1 Tan X Trigonometric Identity Solve Hindi Youtube
· One answer is to say that, properly, the identity is $\sec^2x=1\tan^2x$, where the sides fail to be defined at the same values Share Improve this answer Follow edited Nov 27 '15 at 2246 Joel Reyes Noche 9,278 2 2 gold badges 28 28 silver badges 70 70 bronze badges answered Nov 27 '15 at 1341 Henry Towsner Henry Towsner 106k 1 1 gold badge 30 30 silverGrrrrrI could get a little help from the tutors in the Math Lab on campus but we've been instructed not to seek them out for this problem (and another I am


Topic Lesson Trigonometric Functions


True Or False The Equation Sec 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Is An Identity Brainly Com


Simplify The Trigonometric Expression Tan 2x Tan X Using Double Angle Identities A Brainly Com
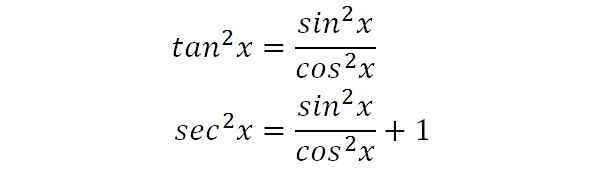


Integrate Sec 2x Method 2


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora



Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia


Solved In Exercises 15 22 Prove The Identity 2



7 4 Proving Trigonometric Identities In This Unit We Ll Be Using Some Formula S That Are Also Found And Used In Unit 7 2 And 7 3 Here We Ll Be Solving Problems To Show That Both Sides Of The Equation Equal Each Other These Formulas Will Help Solve Some Trig


How Can One Prove That Math Tan 2x 2 Cot X Tan 2x Cot 2 X Math Quora


Bestmaths Online Proof 4


How To Solve Tan 2xsin 2x Tan 2x Sin 2x Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities Youtube
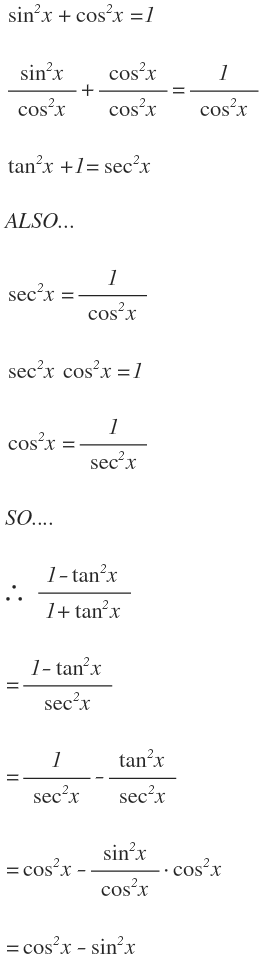


How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic
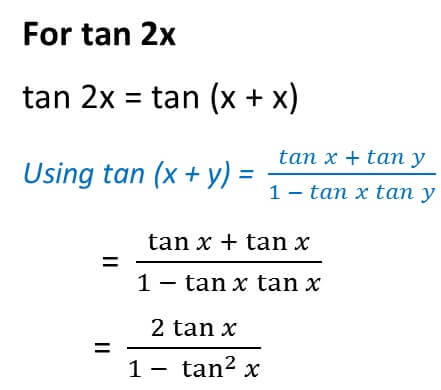


Double Angle Formulas Trigonometry Teachoo 2x 3x Formula Provi



Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia


Prove The Identity Secxcscx Tanx Cotx 2 Tan 2x Cot 2x1 Apply The Distributive Property2 Apply The Brainly Com


Ch Ppt Download



How Do You Verify 4tan 4 Tan 2x 3 Sec 2x 4tan 2x 3 Kinda Hard Please With All The Steps Thanks Socratic


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora


Trig Identities Hsn Forum


Trig Identities Hsn Forum


Ilectureonline


Double Angle Formula And Half Angle Formula Video Lessons Examples And Solutions


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora


7 Proving Ids Trig Functions Identities



14 2 Trigonometric Identities


Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 29 Of 57 Formula For Lowering Power Tan 2 X Youtube
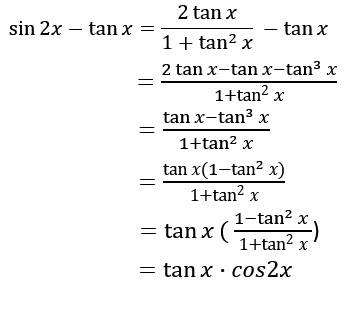


Sin2x Tanx Complete The Identity Socratic
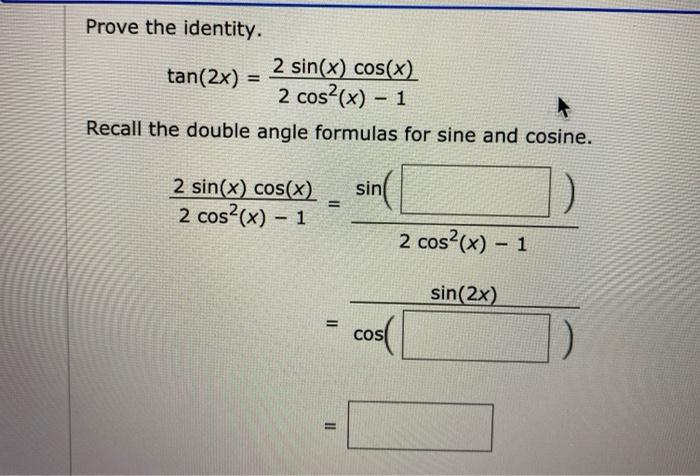


Solved Prove The Identity 2 Sin X Cos X Tan 2x 2 Co Chegg Com
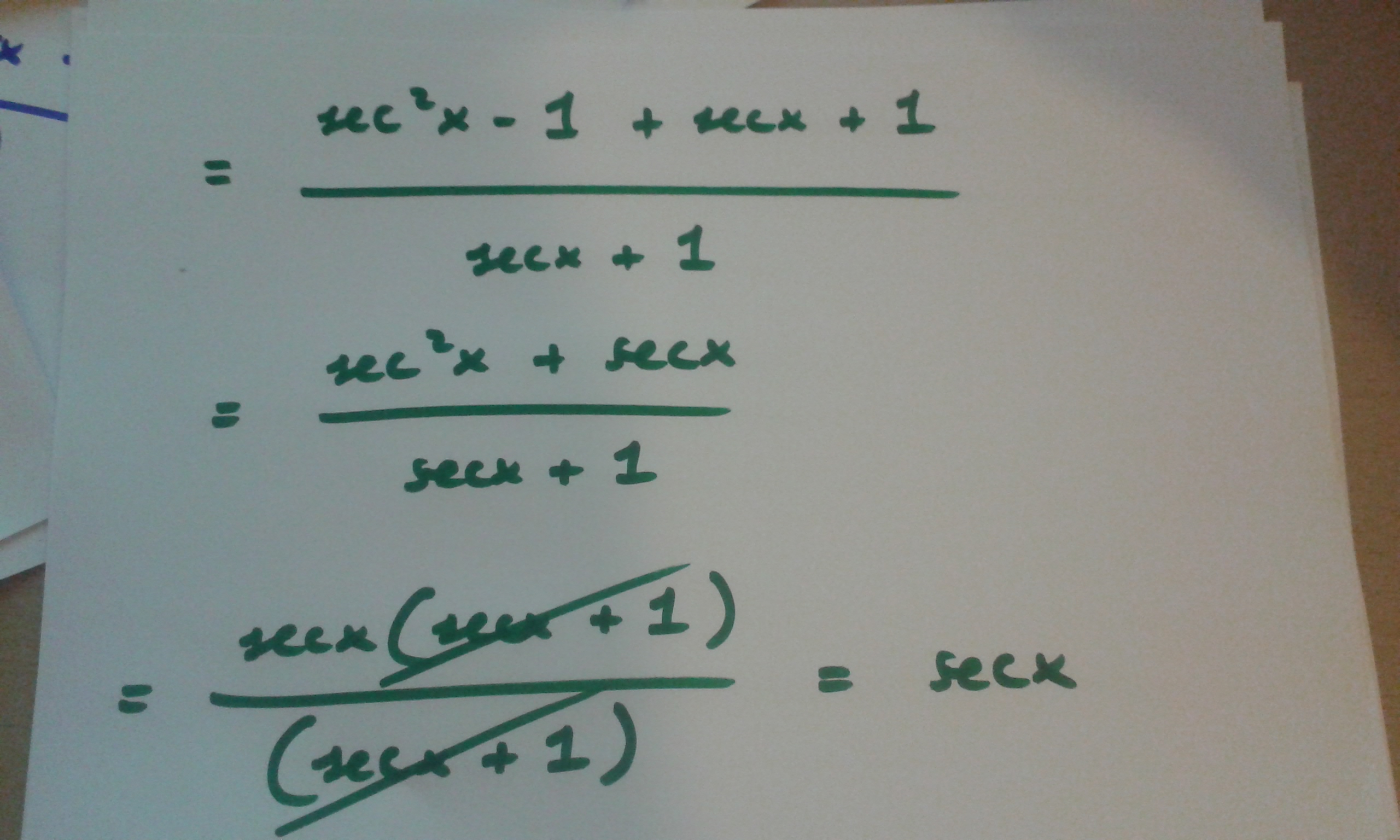


How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic



7 2 47 Integral Of 1 Tan2x Sec2x Cute766



F 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Cos2x 1 Sec 2x 2tanx 2


How To Prove The Identity Tan2 X Sin2 X Tan2 X Sin2 X Quora



Every Day I M Calculatin I D3 Unit Q Pythagorean Identities



The General Solution Of The Equation Tanx Tan 2x Tan 2x Tanx 2 0


6 1 2 Trigonometric Identities
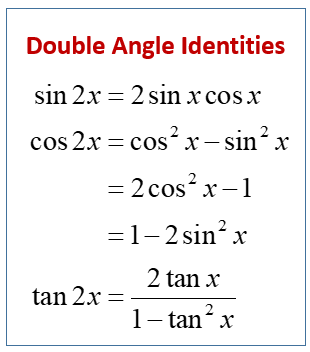


Double Angle Identities Solutions Examples Videos Worksheets Games Activities



2sinxcosx Identity Gamers Smart



1 Tan 2x 1 Cos 2x Sin 2x 2sin 4x 1 Sin 2x Trigonometric Identities Mcr3u Youtube


Solved Complete The Sentence So The Result Is An Identity Let X Be Any Real Number 1 Sin 2 X Cot 2 X Cos 2 X Sec 2 X Tan 2 X Complete The Sent Course Hero



Tan 2x Csc 2x Tan 2x 1 Problem Solving Solving Identity



Solve Tan 2 X 1 0 Yahoo Answers Noha Matthieu Lire Un Livre



Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia



Solved Verify That The Equation Is An Identity Tan 2x Chegg Com
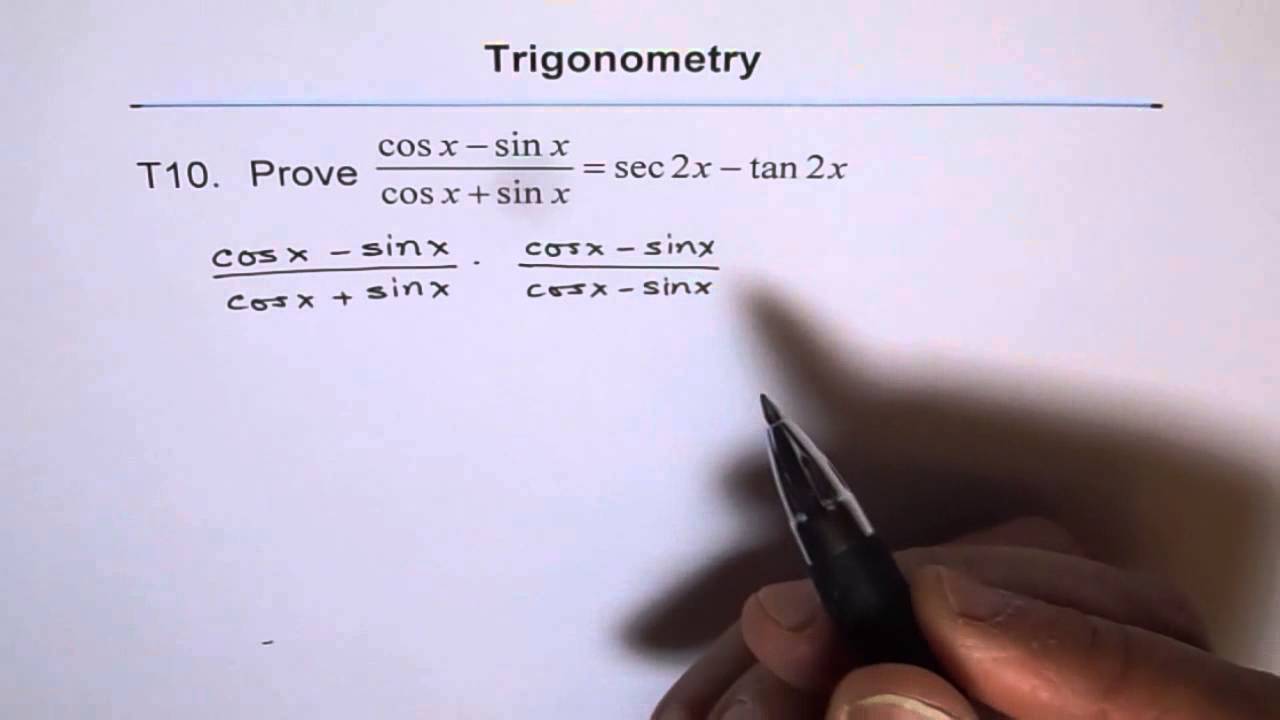


Trig Identity Sec2x Minus Tan2x T10 Youtube



Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像


Solved Consider The Possible Identity Tan 2x Cos 2x 1 Cos 2x Sec 2x A State Any Non Permissible Values B Attempt To Verify Possible Identity Course Hero



Double Angle Properties Rules Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
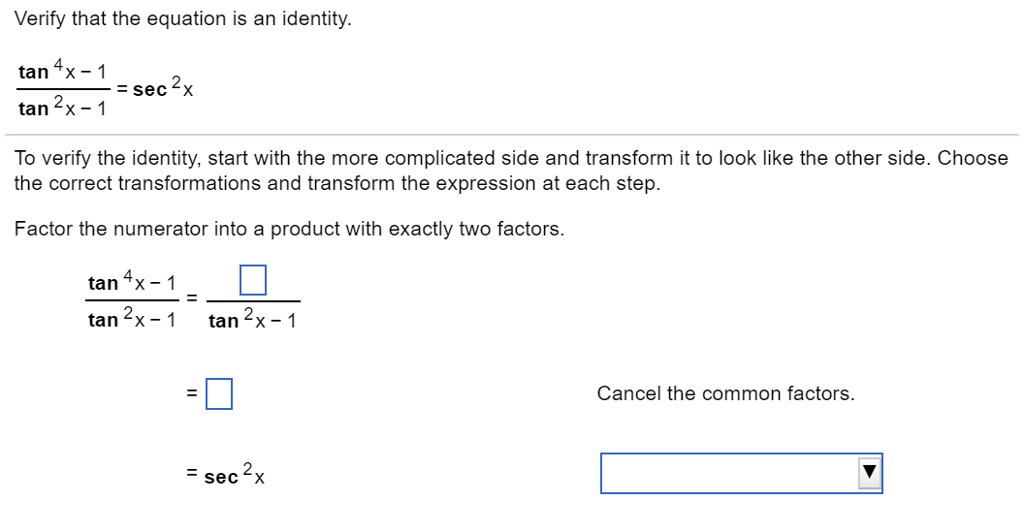


Solved Verify That The Equation Is An Identity Tan 4x 1 Chegg Com
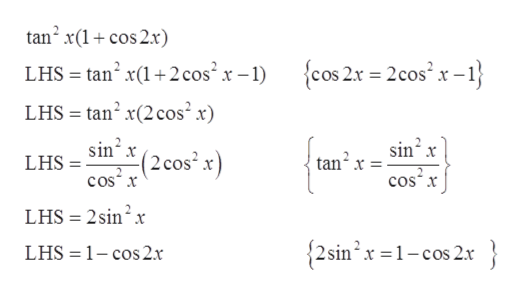


Answered Tan2x 1 Cos2x 1 Cos2x Verify The Bartleby
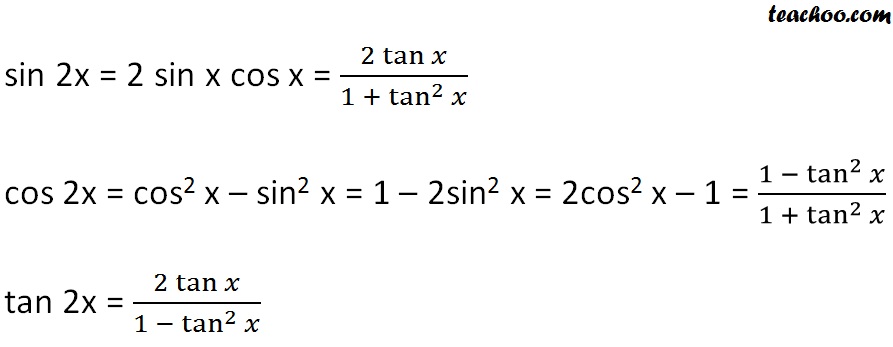


Double Angle Formulas Trigonometry Teachoo 2x 3x Formula Provi



9 1 Identities And Proofs Ppt Download
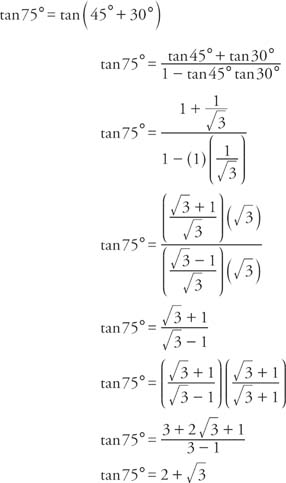


Tangent Identities



Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia


Ilectureonline


Solution Show All Steps Necessary To Verify The Trigonometric Identity 1 Tan 2x Csc 2x Tan 2x
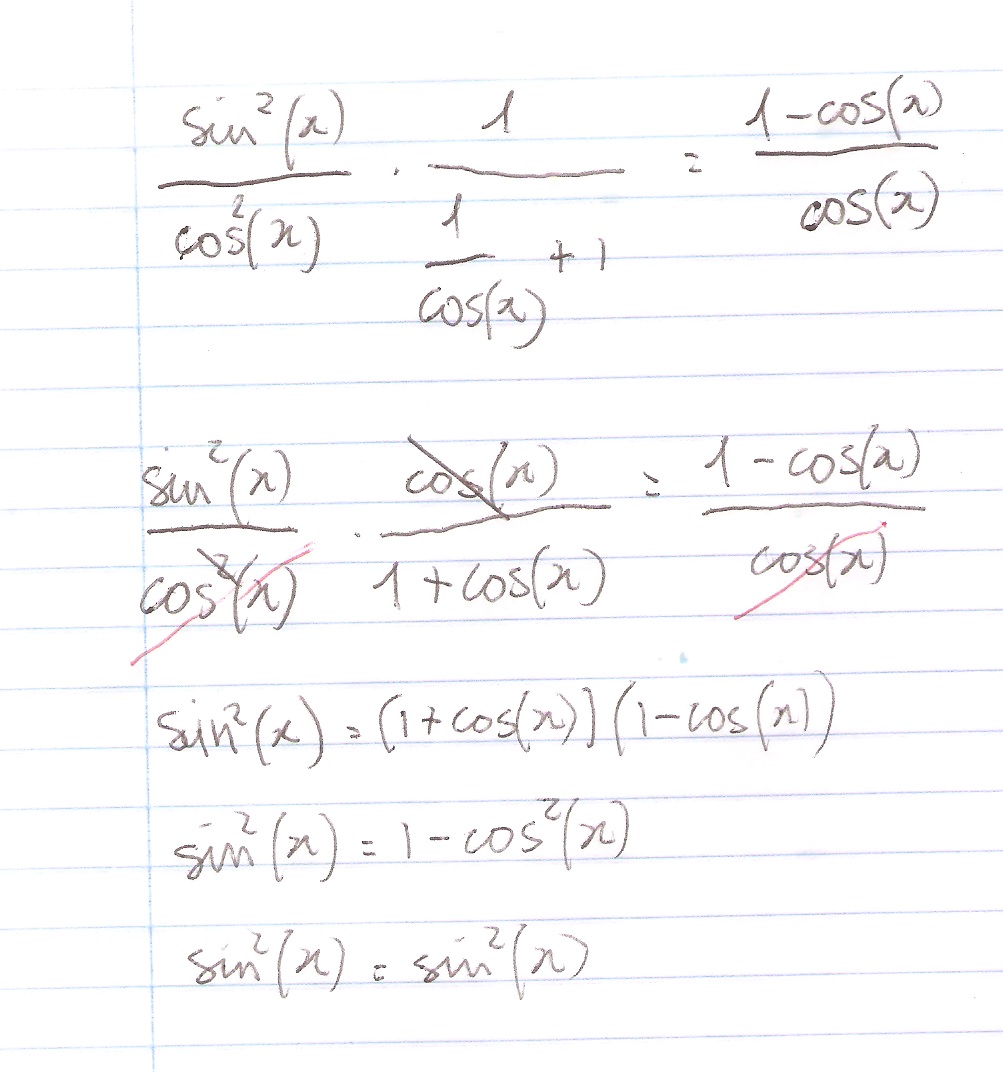


How Do You Prove The Identity Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Socratic


Answered Verify The Identity 2 Tan X 1 Bartleby


Trigonometric Functions Expressed By The Tangent Of The Half Angle Trigonometric Identities


Answered O Trigonometric Identities And Bartleby



Show That The Following Are Not Trigonometric Identities 1 Tan 2x 2tan X 2 Sec X Sqrt 1 Tan 2 X 3 Sin X Y Sin X Sin Y Study Com



Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia
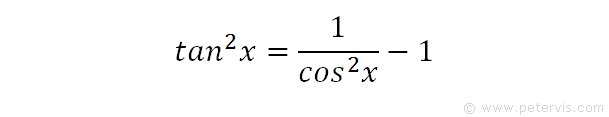


Integrate Tan 2x


Sum And Difference Identities Video Lessons Examples And Solutions



Trig Identities And Formulas Pre Calculus Quiz Quizizz
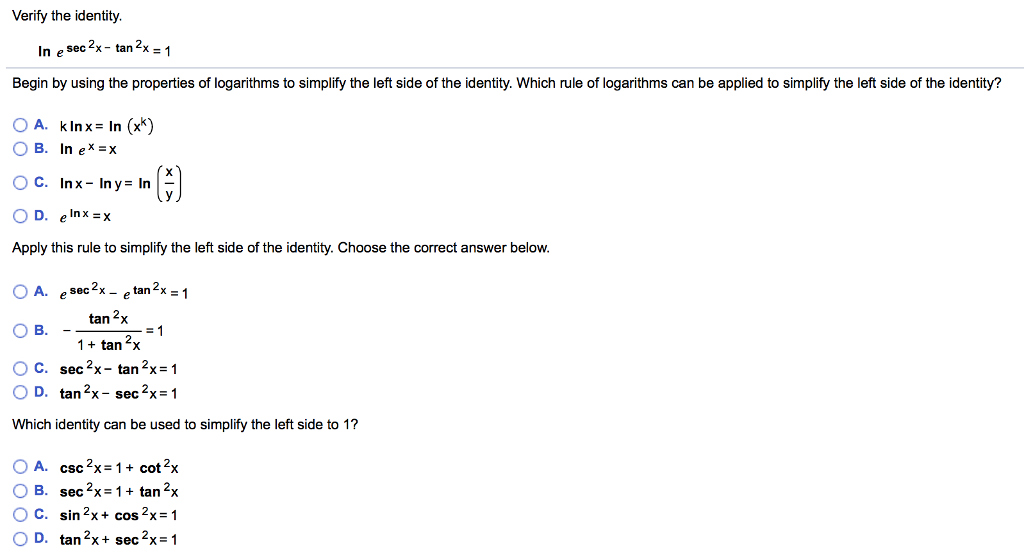


Solved Verify The Identity In Esec 2x Tan 2x 1 Begin By Chegg Com
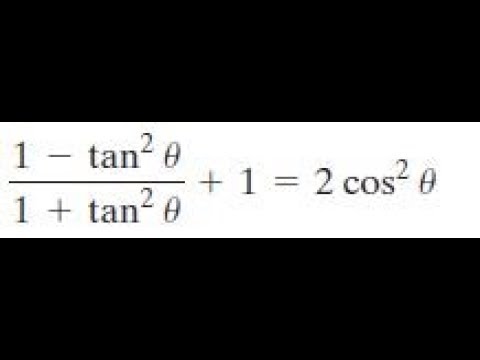


1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2 X 1 2cos 2 X Youtube
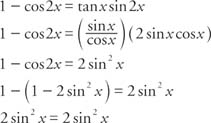


Double Angle And Half Angle Identities



Solved Evaluate Integral Tan 6 2x Sec 4 2x Dx If We Chegg Com



Integrate Tan 2x By Parts
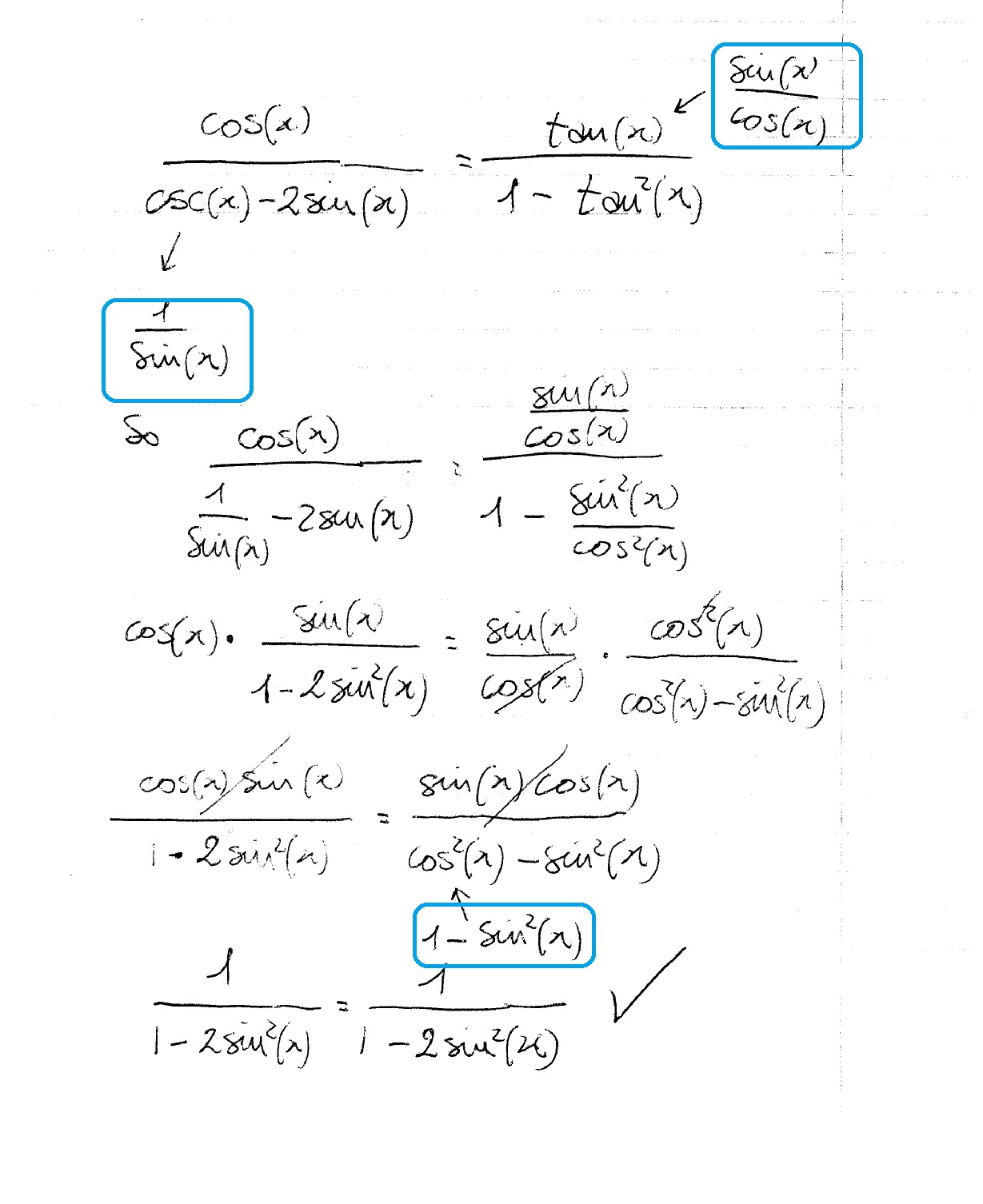


How Do You Prove Cosx Cscx 2sinx Tanx 1 Tan 2x Socratic


Prove That Cos2x Cos 2x Sin 2x 2cos 2x 1 1 2sin 2x 1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
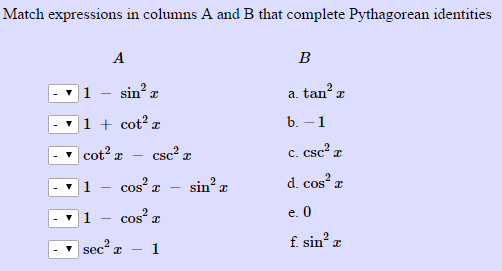


Solved Match Expressions In Columns A And B That Complete Chegg Com
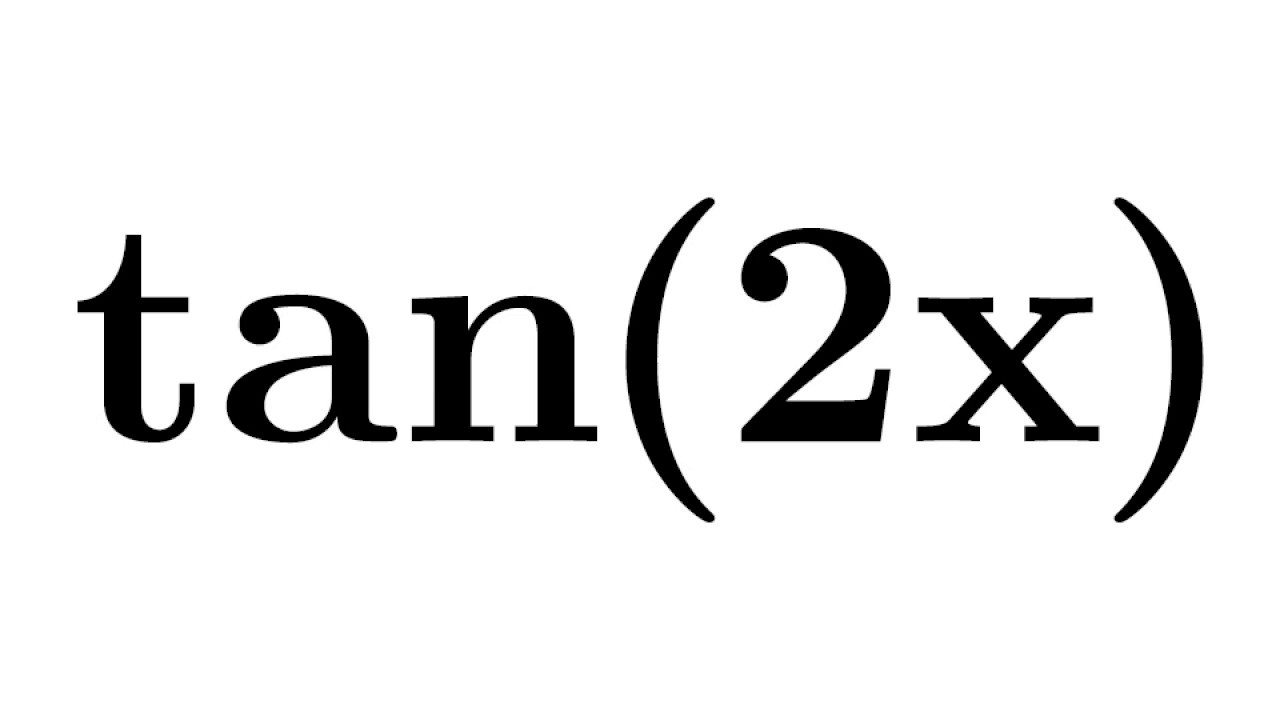


Tan2x Tan 2x Identity For Tan2x Proof Of Tan2x Identity Formula For Tan2x Youtube



How To Use Trig Identities Mathematics Stack Exchange



How Do You Prove The Identities Cosx Secx Sinx Cscx Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿